normal end tidal co2 dog
Examples of some common capnograms are. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar
It has been recognized that monitoring respirations in patients during sedation for out of the operating room procedures is valuable in preventing the occurrence of hypoxic episodes.

. A more complete picture of carbon dioxide transfer can be obtained from a capnogram similar to an ECG tracing. End-tidal CO 2 monitoring is a non-invasive means of estimating arterial CO 2. However an excess of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream can lead to an abnormal condition causing symptoms ranging from dizziness to convulsions.
It is the measurement of CO2 at the completion of exhalation and roughly correlates to the CO2 present in arterial blood. Two private specialty referral hospitals. What is normal end tidal CO2.
Carbon dioxide during ventilation. End-tidal carbon dioxide levels correlate fairly well with arterial carbon dioxide PaCO 2 in birds and mammals. Causes of High End-Tidal CO2 ETCO2 45 mm Hg Clinical Conditions.
Most anesthetics are respiratory depressants and end-tidal CO2 allows early detection of respiratory impairment so appropriate intervention can occur before the problem becomes life threatening. Two private specialty referral hospitals. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
Capnography in Veterinary Sedation. Variants of normal ETCO2 tracings from normal anesthetized animals. This is end-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 which is normally 35 to 45 mm Hg in dogs and 28 to 32 mm.
Throughout the breath cycle. According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg. The end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PetCO2 measured after a single large tidal-volume breath 15 mlkg body weight was compared to simultaneous measurements of PaCO2 in 6 dogs with normal lungs who were receiving high-frequency jet ventilation HFJV.
Normal arterial blood pressure values for dogs and cats are indicated in Table 111. End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Since EtCO 2 correlates well with cardiac output EtCO 2 monitoring during CPR to evaluate efficacy of chest compressions is reasonable if minute ventilation is held constant IIa-B. To determine whether the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide PetCO 2 could predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in patients with cardiopulmonary arrest CPA undergoing CPR.
The number represents capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective.
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. There was an excellent linear correlation b. The patient is hypoventilating or apneic.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Waveform capnography represents the amount of carbon dioxide CO 2 in exhaled air which assesses ventilation.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. Thirty-five client-owned dogs and cats in CPA in which CPR was. This is an important.
End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring ETCO2 has clinical uses far beyond solely determining hypo- or hyperventilation. The value of monitoring respirations using capnography has migrated to veterinary anesthesia to protect lives of precious animals. The patient is experiencing malignant hyperthermia.
Normal end tidal co2 dog Monday April 25 2022 Edit The measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 allows the continuous monitoring of the adequacy of ventilation. The normal amount of carbon dixide in the arterial blood is 35-45 mm Hg a measurable unit of pressure. 35-45 mmHg End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg.
It consists of a number and a graph. Under most circumstances healthy pet no chest surgery end-tidal CO 2 is typically 5 10 mmHg less than arterial CO 2. More Than Just a Number.
Medications Common anesthetics may cause hypoventilationapnea. Left untreated a state of hypercapnia can lead to death. In a review study of 1281 dogs undergoing general anesthesia 63 of dogs experienced hypoventilation.
Common narrow plateaus seen during. 259 Additionally ROSC will cause a sharp increase in EtCO 2 and EtCO 2 monitoring should be used as an indicator of. This non-invasive monitor can give valuable information about cardiac output perfusion and ventilation.
The CO 2 waveform is a valuable tool for detecting leaks in the anesthetic system rebreathing of CO 2. The end-tidal level of carbon dioxide is generally less but is reflective of carbon dioxide in arterial blood and can serve as an indirect noninvasive method of assessing the adequacy ventilation. The measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 allows the continuous monitoring of the adequacy of ventilation and circulation in the anaesthetised patientIt measures inspired and expired carbon dioxide CO 2 throughout the whole respiratory cycle using infrared spectroscopyETCO 2 can be of value in the assessment of ventilation metabolism and of a.

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar
Did You Know Hypercapnia Is Synonymous With Hypoventilation
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar
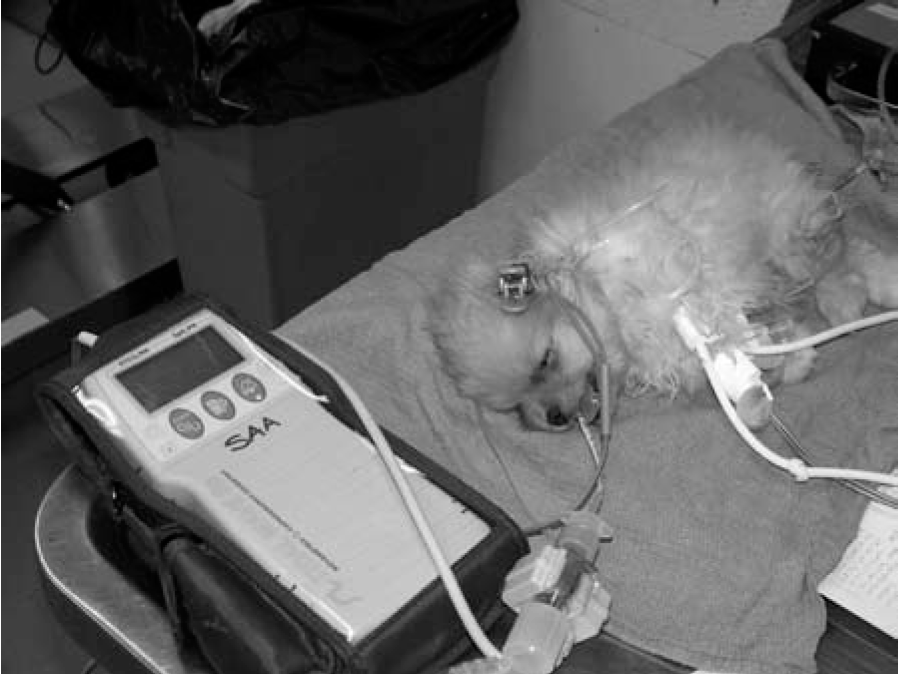
Capnography In Veterinary Medicine Chapter 28 Capnography

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall
